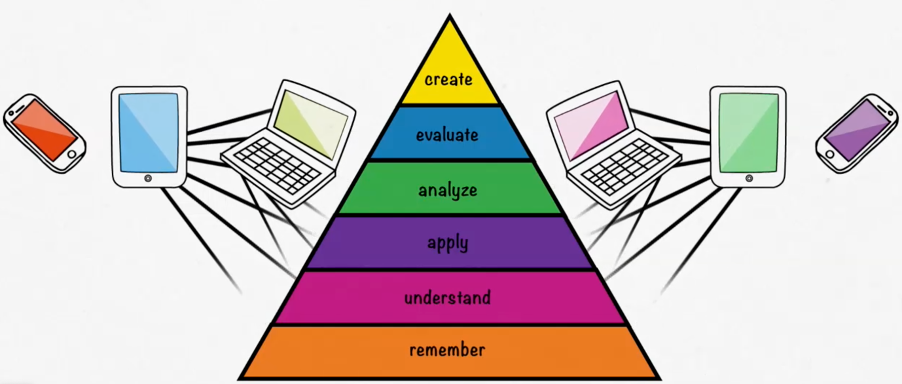
The new normal the we live in now forced teachers to change the way they teach completely, as the virtual schools and classes have obliged them to adapt new strategies and create tools to deliver their lessons successfully.
For decades, Bloom’s Taxonomy has been one of the most reliable tools that teachers have been counting on in every concept they teach to enhance their students’ skills from the lowest order of thinking to the highest . The main challenge that faces most teachers now is how to implement Bloom’s taxonomy in a digital lesson?

What is Bloom’s Taxonomy?
Let’s get back to where it all started. Bloom’s Taxonomy was created in 1956 by the American psychologist Benjamin Bloom to improve communication between the ones who create curricula and the ones who make the examinations. Bloom’s taxonomy quickly became popular not only as a tool to create exams and curricula, but also to validate and formalise teaching and learning practices.
In 2001, it was revised by a number of scientists including Anderson and Kornwhall and had few changes made to it.

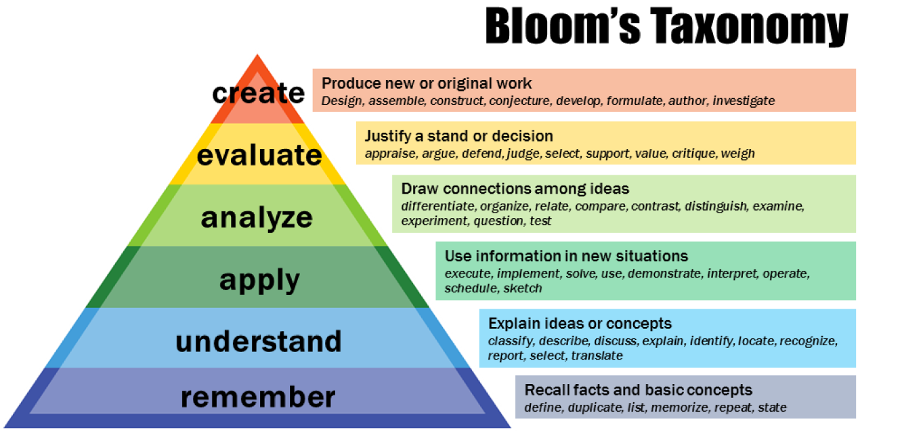
Looking at the original taxonomy: It was formed of 6 cognitive levels, starting from knowledge, followed by comprehension, application, analysis, synthesis reaching the highest order thinking skill Evaluation.

The main modifications done to it in 2001 was changing the noun forms to verb forms and switching evaluation with “synthesis”, which is now referred to “create”.
So what’s the purpose of each level?
Here’s a simple example of how to apply Bloom’s Taxonomy in an ESL lesson:
When you teach your students the names of colors in English for the first time, the first thing they’ll learn is to “remember” the name of each color. By linking each color’s name with its photo, you’ll be moving your students to the next level, which is “understanding”.
But what if you ask them to arrange the colors as in a rainbow? In this case you’ll be moving to the next level which is “applying”.
And if you ask them what’s the difference between lemon yellow and banana yellow for instance, you’re taking them a step higher to “analyzing”.
If you wanna go further, you can simply ask them to justify why they think lemon yellow is better than banana yellow in fashion and if you ask them to color code their portfolios for example. At this point, you’ll be taking them to the top of the taxonomy as they “justified” their choices and “created” an original work.
Is it really that simple?!

Bloom’s Taxonomy has more than one dimension actually, where you can merge the knowledge dimension with the cognitive dimension of the taxonomy.
As shown above, by asking your students to list the secondary colors for example; you’re actually merging remembering with factual knowledge, going up till the top of the pyramid when you asked them to create their color coded portfolios and that’s where the creation dimension is merged with the metacognitive one ( which involves self awareness).
But how to integrate technology into all of this?!

Bloom’s digital taxonomy provides teachers with tools to facilitate the students’ learning in the digital world we live in now, but first, you have to know your students’ digital abilities. Most of our students are experts in using technology these days, you may even ask them to help you out if you’re stuck in a certain website or application. This gives you a great opportunity to get them more engaged and interested in the classroom.
So, getting them to use technology in every step of the way through bloom’s Taxonomy requires them to acquire certain technological skills, for example If you want them to create a digital mind map to analyze the color shades, they need to be able to create a digital mind map, and to create a video , they should have basic knowledge of directing, filming or podcasting.
The Pedagogy Wheel diagram

Here you can see a huge updated list of apps and websites that can get your students to achieve every stage of the taxonomy.
The pedagogy wheel Combines digital tools for Bloom’s Taxonomy with the digital verbs/abilities for each stage along with the most recent apps to be used in each stage. It also connects the Taxonomy with SAMR Model, which is a framework that categorizes four different degrees of classroom technology integration.
Resources:
- https://www.commonsense.org/education/
- https://designingoutcomes.com/english-speaking-world-v5-0/
- https://teachonline.asu.edu/2016/05/integrating-technology-blooms-taxonomy/
- https://www.teachthought.com/critical-thinking/3-dimensional-model-blooms-taxonomy/
- https://thesecondprinciple.com/essential-teaching-skills/blooms-taxonomy-revised/
2 thoughts on “Integrating Technology to Bloom’s Taxonomy”